
PPT Chapter 5 International Trade PowerPoint Presentation ID340584
Comparative advantage is the ability of a country to produce a good or service for a lower opportunity cost than other countries. Opportunity cost measures a trade-off. A nation with a comparative advantage makes the trade-off worthwhile. This means the benefits of buying its good or service outweigh the disadvantages.

Comparative Advantage Example Top 4 Real World Examples
Comparative advantage is where a nation is able to produce a product at a lower opportunity cost. In other words, a nation sacrifices less of Good A to produce Good B than other nations. This is in sharp contrast to absolute advantage because a nation can have a comparative advantage but not actually be more efficient than other countries.

PPT What is Comparative Advantage? PowerPoint Presentation, free
Comparative advantage stipulates that countries should specialize in a certain class of products for export, but import the rest - even if the country holds an absolute advantage in all products. See the entry on positive- and zero-sum situations for a brief explanation of why. Another area where we see this applied is the division of labour.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/comparativeadvantageterm-c052ba19912947f48a59bc277437aeb9.gif)
What Is Comparative Advantage?
Comparative Advantage and Free Trade. Comparative advantage is a key principle in international trade and forms the basis of why free trade is beneficial to countries. The theory of comparative advantage shows that even if a country enjoys an absolute advantage in the production of goods, trade can still be beneficial to both trading partners.

What Is A Comparative Advantage? The Comparative Advantage In A
Comparative advantage is an economic theory created by British economist David Ricardo in the 19th century. It argues that countries can benefit from trading with each other by focusing on making the things they are best at making, while buying the things they are not as good at making from other countries. This theory is based on the idea that every country has different cost structures and.
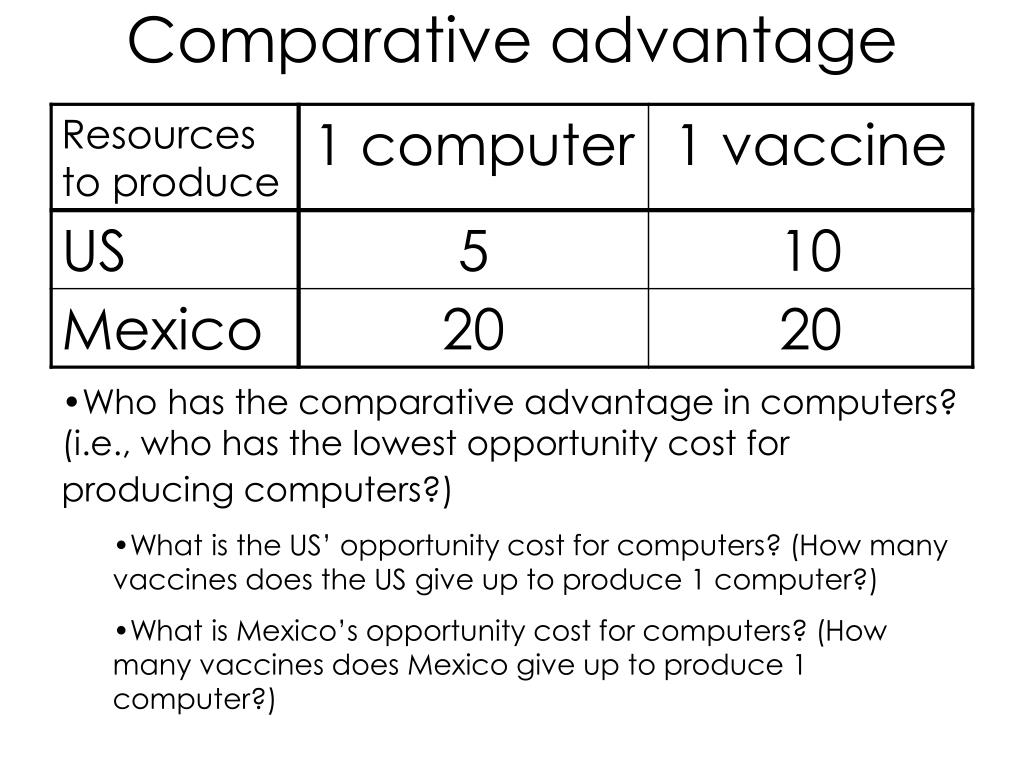
PPT Comparative Advantage PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Yes, all it requires is that the comparative advantage i.e. opportunity cost of making that good for Country A is lower than Country B, regardless of absolute figures. E.g. if country A produces can produce 20 Bananas or 40 Tyres and country B produces 10 Bananas or 30 Tyres.
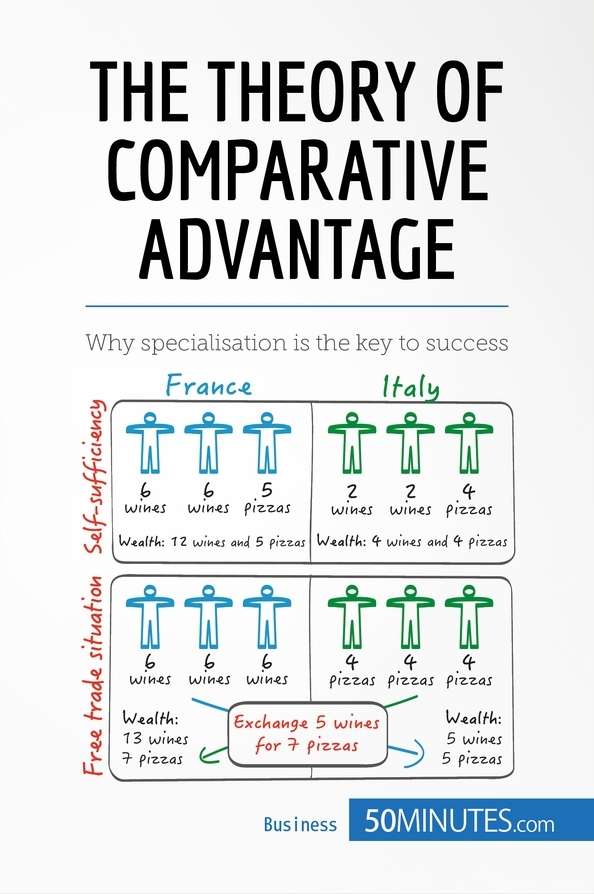
The Theory of Comparative Advantage » Knowledge at your
Comparative advantage in an economic model is the advantage over others in producing a particular good. A good can be produced at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade.

What is comparative advantage YouTube
Comparative advantage fleshes out what is meant by "most best.". It is one of the key principles of economics. Comparative advantage is a powerful tool for understanding how we choose jobs in which to specialize, as well as which goods a whole country produces for export.

Comparative Advantage The Basis of Exchange 1
Comparative Advantage . Comparative advantage takes a more holistic view of production. In this case, the perspective lies in the fact that a country or business has the resources to produce a.

Comparative Advantage YouTube
The theory of comparative advantage is perhaps the most important concept in international trade theory. It is also one of the most commonly misunderstood principles. There is a popular story told among economists that once when an economics skeptic asked Paul Samuelson (a Nobel laureate in economics) to provide a meaningful and nontrivial.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/comparative-advantage-4199071-04ccb37cbf71441ea5264d2c07a48fab.png)
What Is Comparative Advantage?
Comparative advantage acknowledges and attempts to quantify valuable advantages one person, group or corporate entity might have over others, allowing it to be more efficient and productive in a.

Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage ilearnthis
the exchange of goods, services or resources between one economic agent and another. international trade. the exchange of goods, services, or resources between one country and another. gains from trade. the ability of two agents to increase their consumption possibilities by specializing in the good in which they have comparative advantage and.

PPT Comparative Advantage PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Comparative advantage is an economic law referring to the ability of any given economic actor to produce goods and services at a lower opportunity cost than other economic actors. The law of.

PPT Comparative Advantage PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Comparative advantage is a country or company's ability to produce goods and services at a lower opportunity cost than other countries or companies. An opportunity cost is a potential economic benefit that a country or firm loses out on when producing one good or service over another. By producing goods with the lowest opportunity cost.
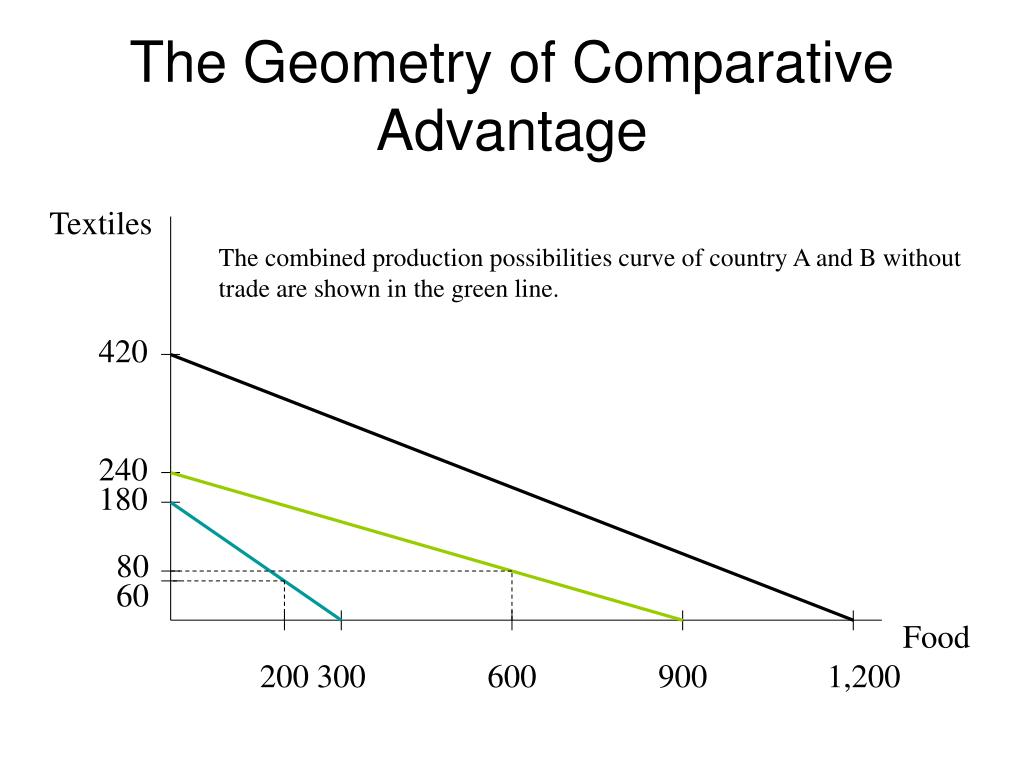
PPT The Theory of Comparative Advantage PowerPoint Presentation, free
Since Saudi Arabia gives up the least to produce a barrel of oil, (1 4 1 4 < 2 2 in Table 33.4) it has a comparative advantage in oil production. The United States gives up the least to produce a bushel of corn, so it has a comparative advantage in corn production. In this example, there is symmetry between absolute and comparative advantage.

PPT Theory of Comparative Advantage PowerPoint Presentation, free
Comparative advantage explains why a country might produce and export something its citizens don't seem very skilled at producing when compared directly to the citizens of another country! (For example, in the past few years India has become a major supplier of phone-answering services for the American market, even though their English.